VNet-VNet example
VNet-VNet connections use VPN gateways to send encrypted traffic between Azure virtual networks. Advantages include:
- Cluster domain name is directly accessible without a NAT.
- VNets from different subscriptions don't need to be associated with the same Active Directory tenant.
Cons include:
- Bandwidth is limited. See the virtual network gateway planning table.
- Configuration is complicated.
- There's an associated cost. See the virtual network gateway planning table.
Example
This example shows how to connect using VNet-VNet connections.
To use this method, you need to create Azure VPN gateways in each connected virtual network.
Note
VPN gateway creation can take up to 45 minutes.
Assume that your cluster is on a subscription called development and is being accessed from a Linux client VM on another subscription called test. It has the following properties:
- Cluster:
- Subscription:
development - Cluster ID:
p-mckwlbakq5 - Account ID:
brcxzr08qr7rbei1 - Organization's domain name:
biganimal.io
- Subscription:
- Linux client VM called
vm-client:- Subscription:
test - Resource group:
rg-client - Virtual network:
vnet-client - Virtual network subnet:
snet-client
- Subscription:
Prerequisites
To walk through an example in your own environment, you need:
Your cluster URL. You can find the URL in the Connect tab of your cluster instance in the BigAnimal portal.
The IP address of your cluster. You can find the IP address of your cluster using the following command:
dig +short p-mckwlbakq5.brcxzr08qr7rbei1.biganimal.ioOutput10.240.1.218
A Postgresql client, such as psql, installed on your client VM.
Step 1: Create a VPN gateway for the cluster's virtual network
In the Azure portal, search for
Virtual network gateways. Locate Virtual network gateways in the search results and select it.On the Virtual network gateways page, select + Create.
On the Create virtual network gateway page, create the VPN gateway for the cluster's resource virtual network
vnet-japaneast. Name the VPN gatewayvpng-biganimal.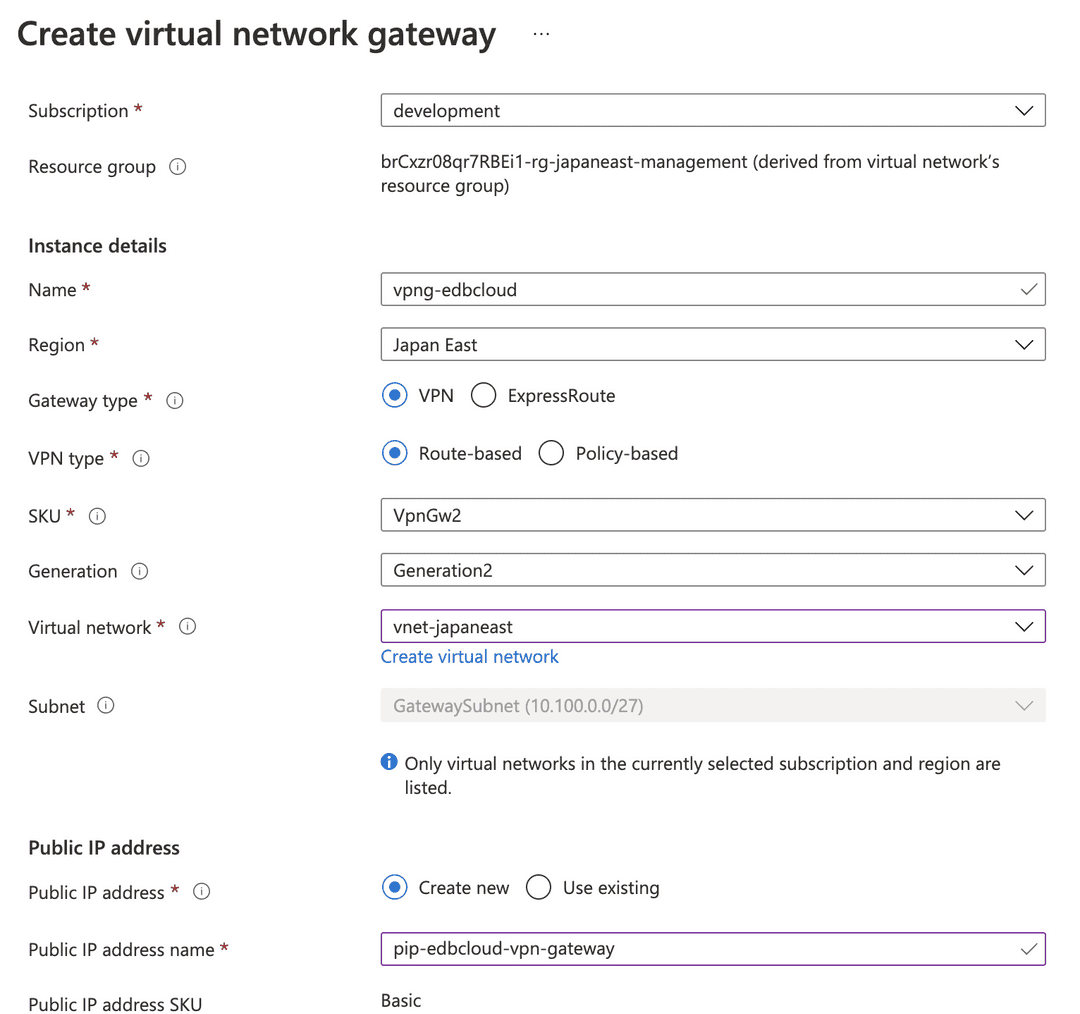
Note
The VPN gateway creates a dedicated subnet to accommodate its gateway VMs. Ensure that your cluster's virtual network address space has enough IP range for the subnet to prevent errors in the virtual network. For more information, see Add a subnet.
Step 2: Create a VPN gateway for the client VM virtual network
In the same way, create the gateway for your client VM virtual network vnet-client. Name the client VPN gateway vpng-client.
Step 3: Add a gateway connection between the two VPN gateways
Use the Azure CLI or PowerShell to add a VPN gateway connection from vpng-biganimal:
Note
The Azure portal allows you to create VPN gateway connections only between virtual networks belonging to the same subscription.
Get the VPN gateway ID of
vpng-client.From the BigAnimal subscription:
az network vnet-gateway show -n vpng-biganimal -g brCxzr08qr7RBEi1-rg-japaneast-management --query "[id]" -otsv
Outputsubscriptions/.../vpng-biganimal
From the client VM's subscription:
az network vnet-gateway show -n vpng-client -g rg-client --query "[id]" -o tsv
Output/subscriptions/.../vpng-client
From the BigAnimal subscription, create a connection from
vpng-biganimaltovpng-client:az network vpn-connection create \ -n vpnc-biganimal-client \ -g brCxzr08qr7RBEi1-rg-japaneast-management \ --vnet-gateway1 /subscriptions/.../vpng-biganimal \ -l japaneast --shared-key "a_very_long_and_complex_psk" \ --vnet-gateway2 /subscriptions/.../vpng-client
Note the value for
--shared-key. It is a PSK for pairing authentication from both sides needed in the next step.From the client VM's subscription, create another connection from
vpng-clienttovpng-ebdcloud:az network vpn-connection create \ -n vpnc-client-biganimal \ -g rg-client \ --vnet-gateway1 /subscriptions/.../vpng-client \ -l japaneast \ --shared-key "a_very_long_and_complex_psk!" \ --vnet-gateway2 /subscriptions/.../vpng-biganimal
Step 4: Verify the connection
After a few minutes, verify the gateway connection status from either virtual networks with the following command:
az network vpn-connection show --name vpnc-client-biganimal -g rg-client \ --query "[connectionStatus]" -o tsv
OutputConnected
Verify the connectivity to the cluster:
dig +short p-mckwlbakq5.brcxzr08qr7rbei1.biganimal.io psql -h p-mckwlbakq5.brcxzr08qr7rbei1.biganimal.io -U edb_admin
Output10.240.1.123 Password for user edb_admin: psql (13.4 (Ubuntu 13.4-1.pgdg28.84+1), server 13.4.8 (Debian 13.4.8-1+deb10)) WARNING : psql major version 13, server major version 13. Some psql features might not work. SSL connection (protocol : TLSV1.3cipherTLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384, bits : 256, compression : off) Type "help" for help. edb_admin=>
- On this page
- Example