FlowServer for WarehousePG architecture
The FlowServer ecosystem consists of three primary components that work together to manage data movement.
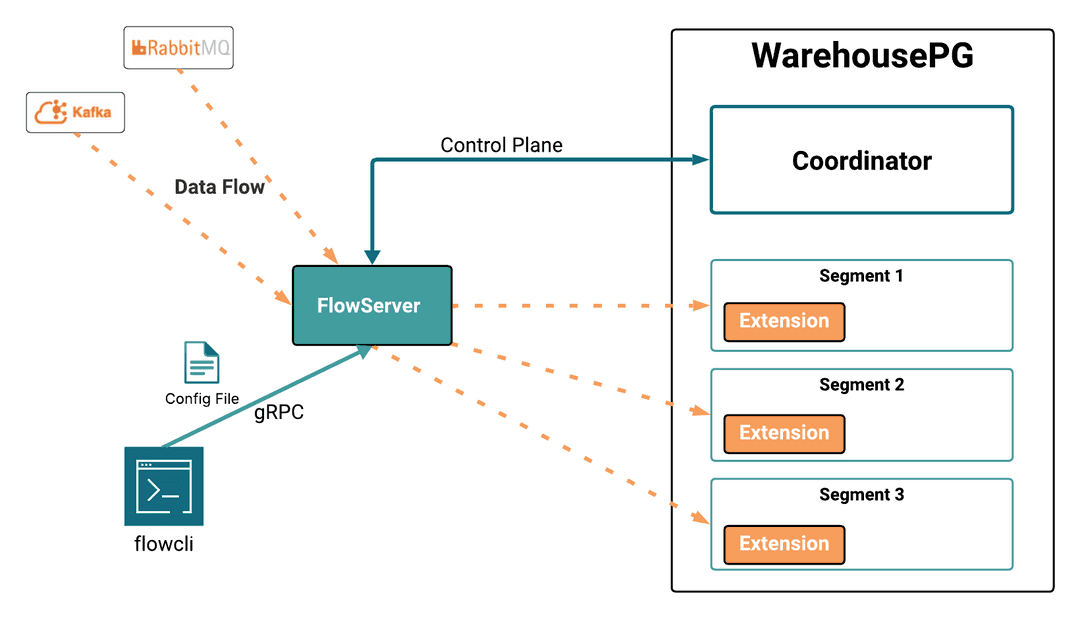
Flowserver
FlowServer is a gRPC-based streaming engine that serves as a central hub for high-speed ETL tasks, receiving data from clients and managing connections to the WarehousePG cluster. Running on any host with cluster connectivity, it handles FlowCLI requests to fetch data from Kafka or RabbitMQ and load it into WarehousePG. The server supports JSON, CSV, and Avro (Kakfa only) formats via configuration files that define database settings. During execution, it submits transactions to the coordinator and uses the gpfdist protocol to write data directly into segments via external tables.
FlowCLI
A dedicated command-line interface used to submit, start, stop, and monitor load jobs. It features optimized subcommands for managing job progress and resetting stream offsets. You can run the FlowCLI commands from any host with connectivity to the WHPG cluster.
Formatter extension
A specialized database extension installed on the WarehousePG segments that handles the high-speed formatting and writing of data directly into the segments.
How FlowServer works
A typical sequence of events for performing an ETL task using FlowServer follows:
- A user initiates one or more ETL load jobs via a client application.
- Flowcli uses the gRPC protocol to submit and start data load jobs to a running FlowServer service instance.
- The FlowServer service instance submits each load request transaction to the WHPG cluster coordinator instance. FlowServer uses the
gpfdistprotocol to store data in external tables that it creates or reuses. - The FlowServer service instance writes the data delivered from the client directly into the segments of the WHPG cluster.
Once the job is started, FlowServer executes the four-stage transformation in real-time.
The multi-stage transformation
FlowServer processes data through a four-stage pipeline to ensure quality and compatibility:
Prepare: FlowServer generates the SQL for external tables and filters out irrelevant raw data at the source.
Format: FlowServer converts incoming raw data from formats like JSON, CSV, or Avro (Kafka only) into a structure compatible with database external tables.
Transform: FlowServer applies the mapping, expressions, and User Defined Functions (UDFs) defined in your configuration file to align data with your target schema.
Load: FlowServer uses the
gpfdistprotocol to write the processed data directly into the WHPG segments, completing the transformation into the final target table.
Could this page be better? Report a problem or suggest an addition!