WarehousePG Observability Architecture
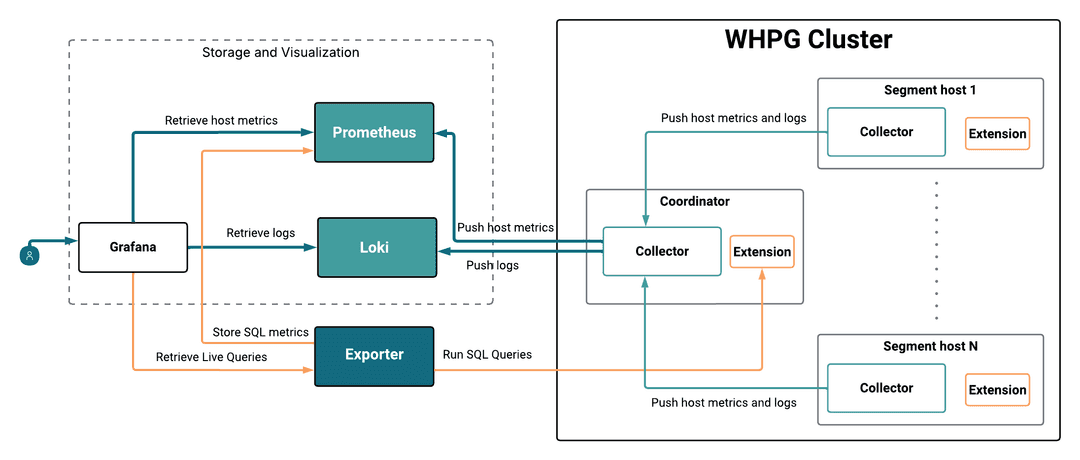
WarehousePG (WHPG) Observability's robust capabilities are built upon the integration of three distinct blocks: an internal data collection layer (Extension and Collector) running within your WHPG cluster, a metric transformation and transport service (Exporter), and external storage and visualization tools (Prometheus, Loki, and Grafana).
WHPG Collector
The WHPG Collector is a service based on Grafana Alloy that runs on the WHPG coordinator, standby, and segments. Each Collector service on the WHPG cluster collects host metrics and log files, and sends them to the Collector service on the coordinator. The Collector service on the coordinator temporarily stores these metrics in memory, then pushes the host metrics to Prometheus, and the log files to Loki.
WHPG Extension
The WHPG Extension is a database extension on your WHPG cluster that creates the observability schema, which includes a number of views and external tables used for SQL metrics. The Extension must be installed in every database from which you want to retrieve metrics.
WHPG Exporter
The WHPG Exporter is a dedicated service which you can install in your WHPG cluster (on the coordinator or standby coordinator) or in an external host.
It runs queries against the observability schema and catalog tables on your WHPG cluster to obtain SQL and cluster-level metrics from each database where the WHPG Extension is installed.
It exposes an endpoint to Grafana for live queries, and pushes the collected data to Prometheus for historic data storage.
Storage and visualization services
WHPG Observability requires a bundle of services to store and visualize the data retrieved from the WHPG cluster. You can install these services to point to your WHPG cluster, leverage an existing installation, or use the following ready-to run stack using Docker Compose to deploy them. The required services are:
Loki: Endpoint for logs. Loki receives data directly from the Collector service on coordinator, and it exposes the data to Grafana.
Prometheus: Endpoint for host metrics and historic SQL metrics. Prometheus receives host level metrics from the Collector, and SQL and cluster metrics from the Exporter.
Grafana: Data visualization service. Grafana reads data from Prometheus and Loki, and fetches real-time data directly from the Exporter. This consolidated data is then presented via our pre-configured dashboards.
How WHPG Observability works
The WHPG Observability workflow has the following phases:
Data collection
Data is collected through two mechanisms:
- The Collector services on the segments gather host metrics and log files locally and send them to the Collector service on the coordinator, which stores them temporarily in memory.
- The Extension on the coordinator creates the
observabilityschema, which contains views and external tables used to extract the required SQL metrics.
Data export and routing
Data is pushed out of the cluster through two distinct paths:
- The Collector service on the coordinator pushes system metrics to Prometheus, and log files to Loki.
- The Exporter queries the WHPG cluster to retrieve the SQL and cluster metrics. It pushes the metrics to Prometheus for historic data storage, and provides an endpoint to Grafana for live data visualization.
Data Storage
Prometheus stores the host metrics from the Collector and the SQL and cluster metrics from Exporter in the Prometheus database.
Loki receives and stores the high-volume log streams pushed by the Collector.
Visualization
Grafana serves as the primary data visualization service, presenting metrics and logs via our pre-configured dashboards to provide immediate operational insight. It retrieves data from three distinct sources:
- Prometheus: provides host metrics and historic SQL metrics.
- Loki: provides log files.
- WHPG Exporter: provides live queries that retrieve instant SQL statistics and cluster-level metrics.
- On this page
- How WHPG Observability works
Could this page be better? Report a problem or suggest an addition!