Using
Suggest editsAfter you configure all of the Thales certificates, you can use them with your EDB Postgres distribution.
Note
This content is intended for versions 15.2 and later of EDB Postgres Advanced Server and versions 15.2 and later of EDB Postgres Extended Server, as these versions support Transparent Data Encryption (TDE).
To implement Thales CipherTrust Manger with your EDB Postgres distribution, you must ensure that you have the following downloaded to your system:
- Python
- pyKMIP
- edb-tde-kmip-client downloaded from your EDB Repos access
You need to copy all of the .pem files that you created in Configuring Thales CipherTrust Manager—key.pem, cert.pem, and ca.pem—to the system where your EDB Postgres distribution is installed. In this example, all of the .pem files and the edb_tde_kmip_client.py program are in the /tmp/ directory.
Check prerequisites and download edb-tde-kmip-client
Ensure that you have the prerequisite software (Python and PyKMIP) installed on your system. See Configuring Thales CipherTrust Manager.
To install the edb-tde-kmip-client on your system, assume root user and issue the install command. This example installs it on a RHEL8 server, so the command is:
dnf install edb-tde-kmip-client
The output looks like this:
[root@ip-172-31-7-145 ec2-user]# dnf install edb-tde-kmip-client Updating Subscription Management repositories. Last metadata expiration check: 0:00:59 ago on Thu 06 Jul 2023 01:30:54 PM UTC. Dependencies resolved. ================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================ Installing: edb-tde-kmip-client noarch 1.0-1.el8 enterprisedb-enterprise-noarch 14 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================ Install 1 Package Total download size: 14 k Installed size: 20 k Is this ok [y/N]: y Downloading Packages: edb-tde-kmip-client-1.0-1.el8.noarch.rpm 23 kB/s | 14 kB 00:00 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total 23 kB/s | 14 kB 00:00 Running transaction check Transaction check succeeded. Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded. Running transaction Preparing : 1/1 Installing : edb-tde-kmip-client-1.0-1.el8.noarch 1/1 Verifying : edb-tde-kmip-client-1.0-1.el8.noarch 1/1 Installed products updated. Installed: edb-tde-kmip-client-1.0-1.el8.noarch Complete!
Create pykmip.conf file
On your system where you have your EDB Postgres distribution, navigate to the directory where you saved your
.pemfiles and theedb_tde_kmip_client.pyclient.In that directory, create a file called
pykmip.conf, and enter the following:- Host
- Port
- Username
- Password
- Keyfile
- Certfile
- Ca_certs
For example:
edb@debian:~$ cat /tmp/pykmip.conf [client] host=172.22.20.194 port=5696 username=testuser123 password=Adminedb@123 keyfile=/tmp/key.pem certfile=/tmp/cert.pem ca_certs=/tmp/ca.pem
Note
For more information on the pykmip.conf file and its contents, see the PyKMIP documentation.
Create a key on Thales CipherTrust Manager
You can create a key with Thales CipherTrust Manager in two ways. You can create one locally with python3 or you can use the Thales CipherTrust Manager UI.
Create a key locally with python3 on Thales CipherTrust Manager
To create the key on Thales CipherTrust Manager, on the system with your EDB Postgres distribution, log in as the database superuser.
Enter
python3, and then enter the following, making adjustments per your system setup and directory paths:
>>> from kmip.pie import client >>> from kmip import enums >>> c = client.ProxyKmipClient(config_file='/tmp/pykmip.conf') >>> c.open() >>> key_id = c.create(enums.CryptographicAlgorithm.AES, 128, name='edbtestkey') (`edbtestkey` is the name that we chose for our TDE master key. Alter this per your naming requirements.) >>> c.activate(key_id) >>> key_id >>> 'key_output_shows_here' >>> c.close()
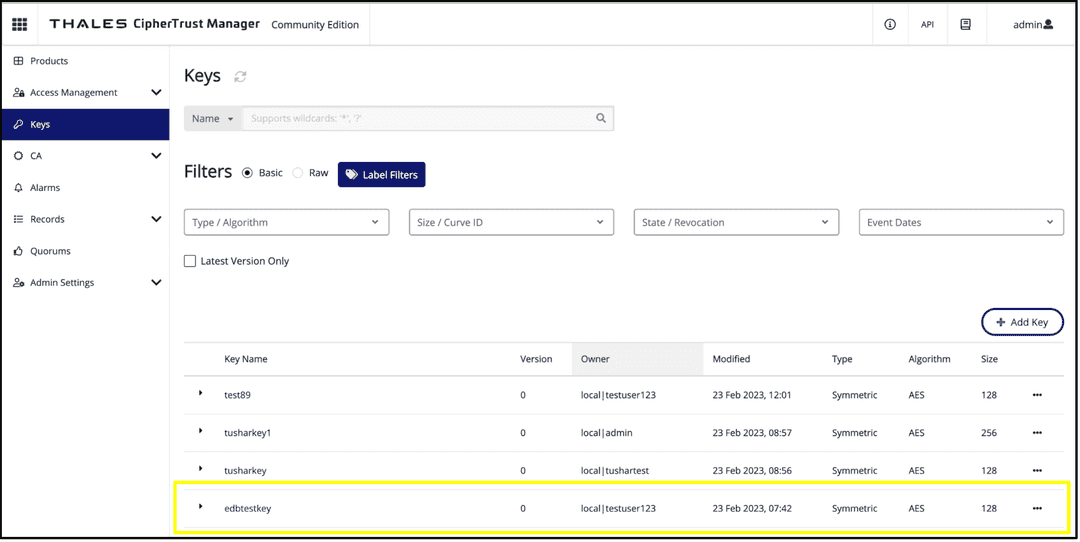
Navigate back to Thales CipherTrust Manager. On the navigation bar, select Keys.
Check that your key, in this case edbtestkey, was created.
Create a key in Thales CipherTrust Manager UI
You can also create keys to use in your database WRAP and UNWRAP commands for encryption in the Thales CipherTrust Manager UI.
Log in to Thales CipherTrust Manager.
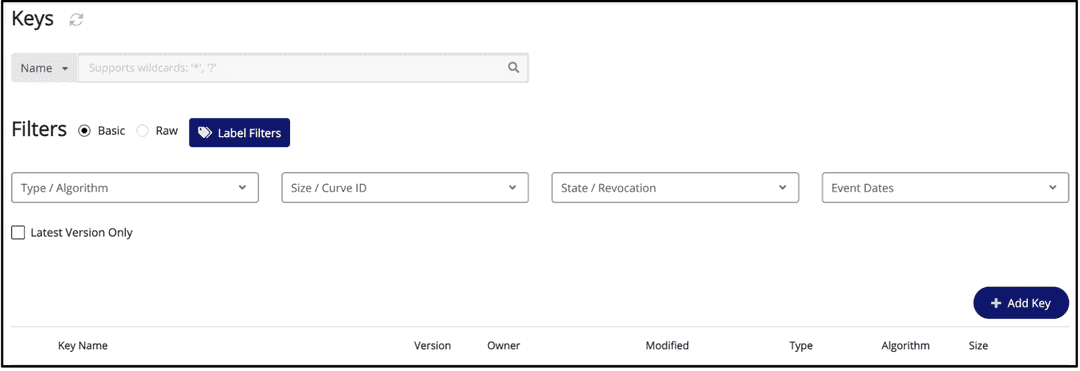
On the main page, from the left bar, select Keys.
To create a key, select Add Key.
Give the key an identifiable name, and select the Key Properties and Key Usage boxes per your requirements.
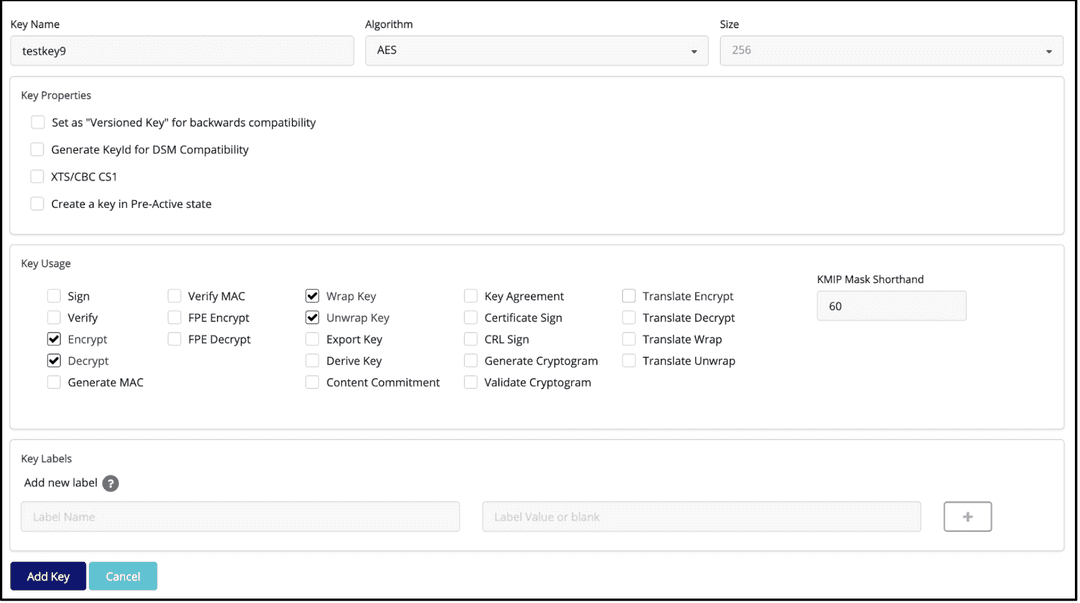
Select Add Key, which brings you to that key's page with specific information.
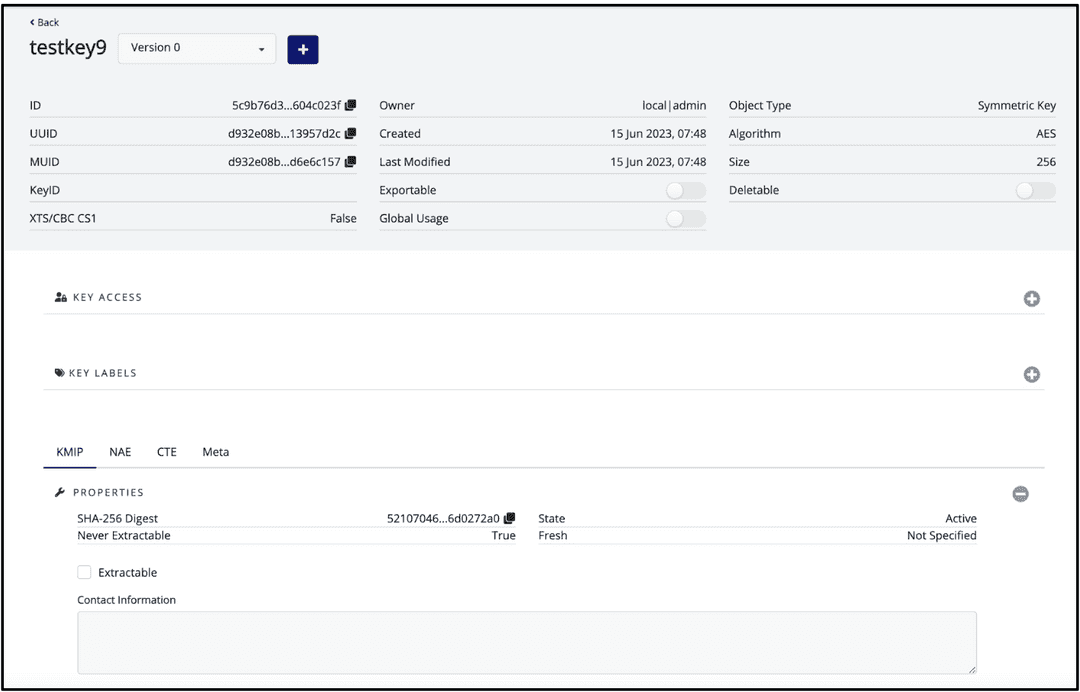
The specific key ID that's needed for your
PGDATAKEYWRAPCMDandPGDATAKEYUNWRAPCMDcommands is the ID that's shown at the top of your key information page.
Verify encryption and decryption
To ensure that the key that you created can encrypt and decrypt data, run the following two commands as the superuser on your system where you have your EDB Postgres distribution.
printf secret | python3 /tmp/edb_tde_kmip_client.py encrypt --out-file=test.bin --pykmip-config-file=/tmp/pykmip.conf --key-uid='key_output_here’ --variant=thales
- Location of the KMIP client:
/tmp/edb_tde_kmip_client.py - Output file:
test.bin - Location of PyKMIP configuration file:
/tmp/pykmip.conf - Encrypted key output: TDE key output
- Variant: Allows for KMIP compatibility with Thales
python3 /tmp/edb_tde_kmip_client.py decrypt --in-file=test.bin --pykmip-config-file=/tmp/pykmip.conf --key-uid='key_output_here' --variant=thales
If this is successful, it produces the output of secret:
printf secret | python3 /tmp/edb_tde_kmip_client.py encrypt --out-file=test.bin --pykmip-config-file=/tmp/pykmip.conf --key-uid='72cb431904fe4dd0a77207b03bff7755be6265cd7f6f463bb0e59023ec5456f4' --variant=thales python3 /tmp/edb_tde_kmip_client.py decrypt --in-file=test.bin --pykmip-config-file=/tmp/pykmip.conf --key-uid='72cb431904fe4dd0a77207b03bff7755be6265cd7f6f463bb0e59023ec5456f4' --variant=thales secret
Perform initdb for the database
After you create the key and verify encryption and decryption, you can export the PGDATAKEYWRAPCMD and PGDATAKEYUNWRAPCMD to wrap and unwrap your encryption key and initialize your database.
Log in to your EDB Postgres distribution system as the database superuser, in this example the enterprisedb user:
sudo su - enterprisedb.Navigate to the
/bindirectory where your executables live. In this example, it's/usr/lib/edb-as/15/bin.Enter:
export PGDATAKEYWRAPCMD='python3 /tmp/edb_tde_kmip_client.py encrypt --pykmip-config-file=/tmp/pykmip.conf --key-uid=key_ouput_here --out-file=%p --variant=thales’
- Enter:
export PGDATAKEYUNWRAPCMD='python3 /tmp/edb_tde_kmip_client.py decrypt --pykmip-config-file=/tmp/pykmip.conf --key-uid=key_output_here --in-file=%p --variant=thales’
In this example:
enterprisedb@ip-172-31-46-134:/usr/lib/edb-as/15/bin$ export PGDATAKEYWRAPCMD='python3 /tmp/edb_tde_kmip_client.py encrypt --pykmip-config-file=/tmp/pykmip.conf --key-uid=72cb431904fe4dd0a77207b03bff7755be6265cd7f6f463bb0e59023ec5456f4 --out-file=%p --variant=thales' enterprisedb@ip-172-31-46-134:/usr/lib/edb-as/15/bin$ export PGDATAKEYUNWRAPCMD='python3 /tmp/edb_tde_kmip_client.py decrypt --pykmip-config-file=/tmp/pykmip.conf --key-uid=72cb431904fe4dd0a77207b03bff7755be6265cd7f6f463bb0e59023ec5456f4 --in-file=%p --variant=thales'
Perform your initdb per your database requirements, for example:
./initdb -D dd12 -y.If all is successful, your output looks like this:
edb@debian:~$ /usr/lib/edb-as/15/bin$ ./initdb -D /var/lib/edb-as/15/dd12 -y
The files belonging to this database system will be owned by user "edb".
This user must also own the server process.
The database cluster will be initialized with locale "en_US.utf-8".
The default database encoding has accordingly been set to "UTF8".
The default text search configuration will be set to "english".
Data page checksums are disabled.
Transparent data encryption is enabled.
creating directory dd12 ... ok
creating subdirectories ... ok
selecting dynamic shared memory implementation ... posix
selecting default max_connections ... 100
selecting default shared_buffers ... 128MB
selecting default time zone ... Asia/Kolkata
creating configuration files ... ok
setting up data encryption ... ok
running bootstrap script ... ok
performing post-bootstrap initialization ... ok
creating edb sys ... ok
loading edb contrib modules ...
edb_redwood_bytea.sql
edb_redwood_date.sql
dbms_alert_public.sql
dbms_alert.plb
dbms_job_public.sql
dbms_job.plb
dbms_lob_public.sql
dbms_lob.plb
dbms_output_public.sql
dbms_output.plb
dbms_pipe_public.sql
dbms_pipe.plb
dbms_rls_public.sql
dbms_rls.plb
dbms_sql_public.sql
dbms_sql.plb
dbms_utility_public.sql
dbms_utility.plb
dbms_aqadm_public.sql
dbms_aqadm.plb
dbms_aq_public.sql
dbms_aq.plb
dbms_profiler_public.sql
dbms_profiler.plb
dbms_random_public.sql
dbms_random.plb
dbms_redact_public.sql
dbms_redact.plb
dbms_lock_public.sql
dbms_lock.plb
dbms_scheduler_public.sql
dbms_scheduler.plb
dbms_crypto_public.sql
dbms_crypto.plb
dbms_mview_public.sql
dbms_mview.plb
dbms_session_public.sql
dbms_session.plb
edb_bulkload.sql
edb_gen.sql
edb_objects.sql
edb_redwood_casts.sql
edb_redwood_strings.sql
edb_redwood_views.sql
utl_encode_public.sql
utl_encode.plb
utl_http_public.sql
utl_http.plb
utl_file.plb
edb_ht_public.sql
edb_ht.plb
utl_tcp_public.sql
utl_tcp.plb
utl_smtp_public.sql
utl_smtp.plb
utl_mail_public.sql
utl_mail.plb
utl_url_public.sql
utl_url.plb
utl_raw_public.sql
utl_raw.plb
commoncriteria.sql
edb_gen_redwood.sql
waitstates.sql
installing extension edb_dblink_libpq ... ok
installing extension edb_dblink_oci ... ok
snap_tables.sql
snap_functions.sql
sys_stats.sql
ok
finalizing initial databases ... ok
syncing data to disk ... ok
initdb: warning: enabling "trust" authentication for local connections
initdb: hint: You can change this by editing pg_hba.conf or using the option -A, or --auth-local and --auth-host, the next time you run initdb.
Success. You can now start the database server using:
pg_ctl -D dd12 -l logfile start
- Start your database, and navigate to your
/datadirectory to view thepostgresql.conffile. Make sure that yourdata_encryption_key_unwrap_command, which you set withexport PGDATAUNWRAPCMD, is present under the Authentication section.
# - Authentication - #authentication_timeout = 1min # 1s-600s #password_encryption = scram-sha-256 # scram-sha-256 or md5 #db_user_namespace = off # GSSAPI using Kerberos #krb_server_keyfile = 'FILE:${sysconfdir}/krb5.keytab' #krb_caseins_users = off # - SSL - #ssl = off #ssl_ca_file = '' #ssl_cert_file = 'server.crt' #ssl_crl_file = '' #ssl_crl_dir = '' #ssl_key_file = 'server.key' #ssl_ciphers = 'HIGH:MEDIUM:+3DES:!aNULL' # allowed SSL ciphers #ssl_prefer_server_ciphers = on #ssl_ecdh_curve = 'prime256v1' #ssl_min_protocol_version = 'TLSv1.2' #ssl_max_protocol_version = '' #ssl_dh_params_file = '' #ssl_passphrase_command = '' #ssl_passphrase_command_supports_reload = off # - Data Encryption - data_encryption_key_unwrap_command = 'python3 /tmp/edb_tde_kmip_client.py decrypt --pykmip-config-file=/tmp/pykmip.conf --key-uid=72cb431904fe4dd0a77207b03bff7755be6265cd7f6f463bb0e59023ec5456f4 --in-file=%p --variant=thales'
For more information on how TDE is incorporated with EDB Postgres Advanced Server and EDB Postgres Extended Server, see the EDB Transparent Data Encryption documentation.
Could this page be better? Report a problem or suggest an addition!