Using
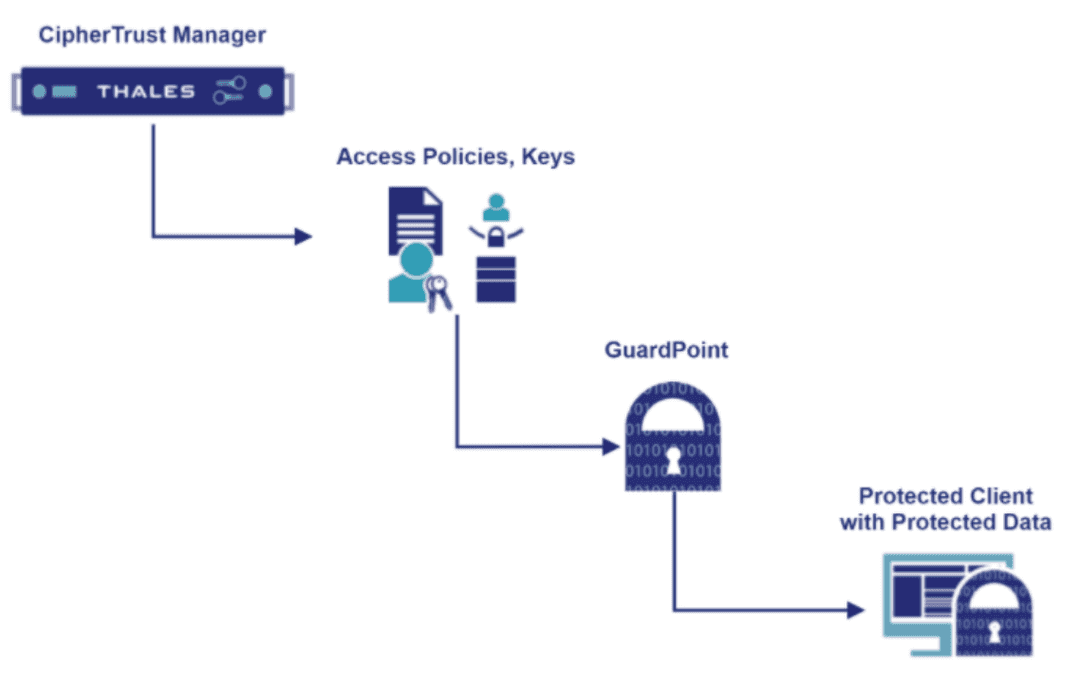
Suggest editsCTE protects data either at the file level or at the storage device level. A CTE agent running on the Postgres host manages the files behind a GuardPoint by enforcing the policy associated with it and communicates data access events to the CipherTrust Manager for logging. A GuardPoint is usually associated with a Linux mount point or a Windows volume but can also be associated with a directory subtree.
The following diagram shows the CTE architecture.
Sample user scenarios
These sample user scenarios show deploying CTE solutions on EDB Postgres Advanced Server and EDB Postgres Extended Server with BDR hosts.
EDB Postgres Advanced Server (single instance)
- Install CTE agent on the Postgres host.
- Log in to the Postgres host and stop the Postgres server.
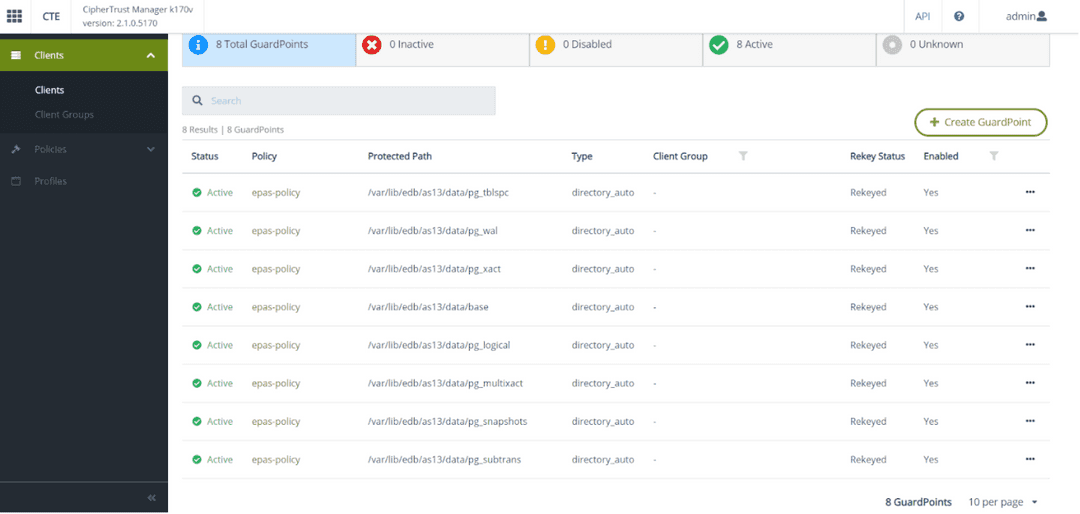
- Create the GuardPoints with the CM web UI using the epas-policy policy on the Postgres host. Set the following directories as the protected path on the EDB Postgres Advanced Server host, assuming PGDATA is set to
/var/lib/edb/as13/dataon the host:
- Restart the Postgres server on the Postgres host as the user enterprisedb. Make sure you're logged in using ssh, not sudo.
EDB Postgres Extended Server with BDR-Always-ON
The following diagram shows the BDR-Always-ON architecture. For more details, refer to the BDR-Always-ON Architecture documentation.
Note
The documentation requires EDB access credentials.

Install CTE agents on all the postgres and barman nodes.
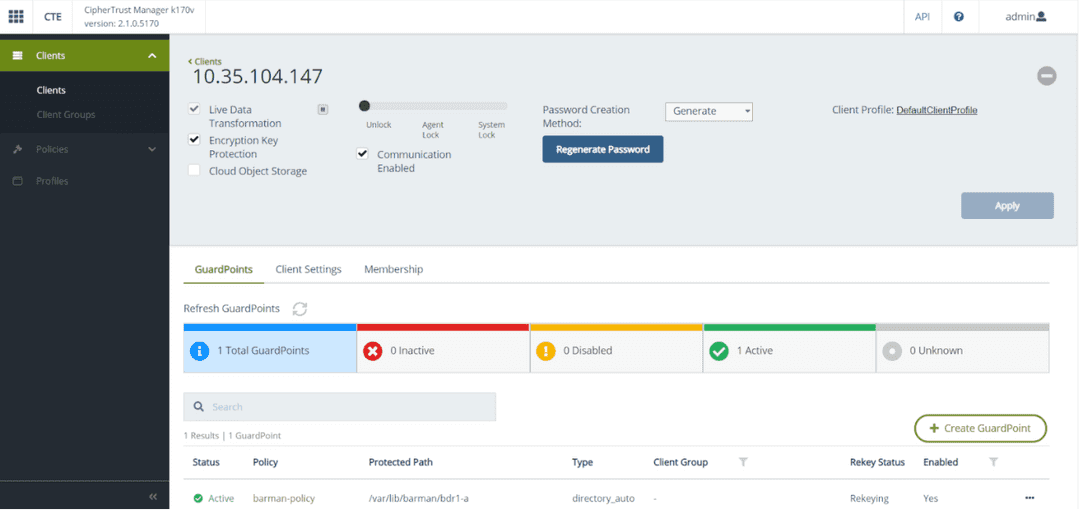
Create a GuardPoint with the CM web UI using the barman-policy policy on the directory
/var/lib/barman/<server-name>on the barman node in data center A (DC A). The following screenshot shows a GuardPoint created for the barman node.
Log in to the standby node in data center A and stop the Postgres server.
Create a GuardPoint on the standby node with the CM web UI using the postgres-policy policy on the PGDATA directory
/opt/postgres/data.Restart the Postgres server on the standby node as the user postgres. Make sure you're logged in using ssh, not sudo.
Log in to the Shadow Master node in data center A and stop the Postgres server.
Create a GuardPoint on the Shadow Master node with the CM web UI using the postgres-policy policy on the PGDATA directory
/opt/postgres/data.Restart the Postgres server on the Shadow Master node as the user postgres. Make sure you're logged in using ssh, not sudo.
Log in to the Lead Master node in data center A and stop the Postgres server.
Create a GuardPoint on the Lead Master node with the CM web UI using the postgres-policy policy on the PGDATA directory
/opt/postgres/data.Restart the Postgres server on the Lead Master node as the user postgres. Make sure you're logged in using ssh, not sudo.
The following screenshot shows a GuardPoint created for Lead Master in data center A.

- Repeat steps 2 through 11 for postgres and barman nodes in data center B (DC B).
- On this page
- Sample user scenarios
Could this page be better? Report a problem or suggest an addition!