Configuring the PEM server to use Windows Active Directory domain services for Kerberos authentication (SSPI) v9
The Windows Active Directory domain service works with hostnames and not with IP addresses. To use single sign-on in PEM Server using Active Directory domain services, configure the following machines with hostnames using the DNS:
- Windows server (domain controller)
- PEM server (PEM web server and PEM backend database server)
- Client machine
For example, if the realm on Windows Active Directory is edbpem.internal, then you can set the Windows server hostname to Krb5server.edbpem.internal, the PEM server hostname to pem.edbpem.internal, and the client's hostname to pg12.edbpem.internal.
1. Install Active Directory, the PEM server, and the PEM backend database server
Perform the following installations:
Install Active Directory on the Windows server (domain controller) that functions as the authentication server. Also, configure the Active Directory domain services to use Kerberos authentication, and then start it.
Install the PEM server on a separate Linux machine. For more information, see Installing the PEM server.
Install the PEM backend database (Postgres/EDB Postgres Advanced Server) on the same Linux machine as the PEM server or a different one. For more information, see the installation steps on the EDB Docs website.
2. Create users in Active Directory to map with service principals
Create users in Active Directory of the Windows server to map with the HTTP service principal for the PEM web application.
Open Active Directory Users and Computers > <DOMAIN_NAME> > Users. Right-click and select New > User.

Enter the user details.
Give the password and make sure to clear User must change password at next logon. Also select User cannot change password and Password never expires.
Review the user details.
On the PEMServer Web Properties dialog box, add the users as members of the Domain Users group:
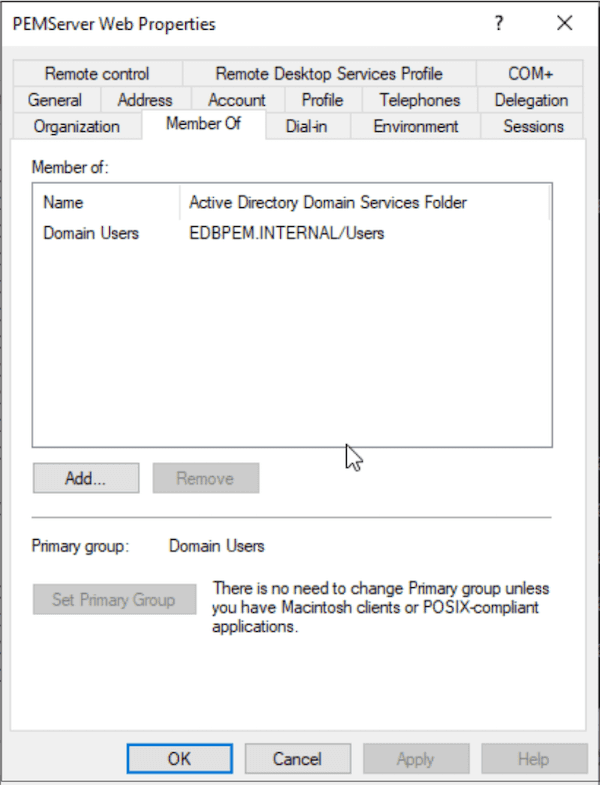
Create the user (for example, pemserverdb) in Active Cirectory of the Windows server to map with the Postgres service principal for the PEM backend database.
3. Extract key tables from Active Directory
Extract the key tables for the service principals and map them with the respective domain users you created.
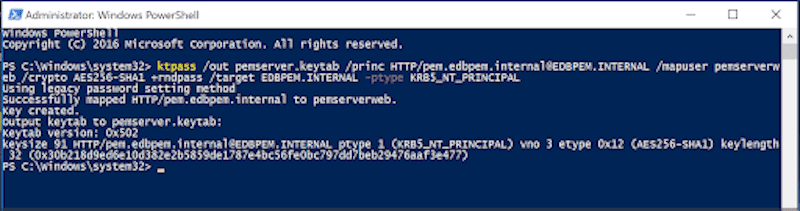
Open Windows PowerShell as an administrator. Create a key table for HTTP service principal mapping with the user pemserverweb and a key table for Postgres service principal mapping with the user pemserverdb:
ktpass /out pemserver.keytab /princ HTTP/pem.edbpem.internal@EDBPEM.INTERNAL /mapuser pemserverweb /crypto AES256-SHA1 +rndpass /target EDBPEM.INTERNAL -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL -kvno 0 ktpass /out pemdb.keytab /princ postgres/pem.edbpem.internal@EDBPEM.INTERNAL /mapuser pemserverdb /crypto AES256-SHA1 +rndpass /target EDBPEM.INTERNAL -ptype KRB5_NT_PRINCIPAL -kvno 0
Where:
pemserver.keytabis the name of the key table for the PEM web application.pemdb.keytabis the name of the key table for the PEM backend database server.pem.edbpem.internal@EDBPEM.INTERNALis the hostname of the PEM server. Here, @EDBPEM.INTERNAL means @REALM.pemserverwebis the user for the PEM web application.pemserverdbis the user for the PEM backend database server.EDBPEM.INTERNALis the domain of the target.
Note
The command line argument
+rndpassresets the password for the domain user pemserverweb to a random password. The/targetoption is optional.On the Accounts tab, add Kerberos support for the user accounts.

!!! Note On the Accounts tab, the user logon name shows HTTP/pem.edbpem.internal@EDBPEM.INTERNAL. The Delegation tab is enabled for the pemserverweb user.
On the Delegation tab, select Trust this user for delegation to any service (Kerberos only) for the users you created.
Copy both the key tables to the PEM server host or to the PEM web server and PEM backend database server hosts if installed on different hosts.
On the PEM server, move the key tables to the required location and change the ownership:
mv /tmp/pemserver.keytab <PEM_INSTALLATION_DIRECTORY>/share chown pem <PEM_INSTALLATION_DIRECTORY>/share/pemserver.keytab
mv /tmp/pemdb.keytab <DATA_DIRECTORY_OF_POSTGRES>/ chown enterprisedb <DATA_DIRECTORY_OF_POSTGRES>/pemdb.keytab
Where:
OS_USERNAME_ON_PEM_SERVERis the name of the operating system user on the PEM server.DATA_DIRECTORY_OF_POSTGRESis the path of the data directory of the installed Postgres database (PostgreSQL/EDB Postgres Advanced Server).
4. Configure the PEM backend database server
Add the key table location in the postgresql.conf file.
krb_server_keyfile='FILE:/<DATA_DIRECTORY_OF_POSTGRES>/pemdb.keytab'
Where DATA_DIRECTORY_OF_POSTGRES is the path of the data directory of the installed Postgres database (PostgreSQL/EDB Postgres Advanced Server).
Edit the krb5.conf file:
```ini
$ sudo vim /etc/krb5.conf
[libdefaults]
default_realm = EDBPEM.INTERNAL
Forwardable = True
[domain_realm]
.edbpem.org = EDBPEM.INTERNAL
edbpem.org = EDBPEM.INTERNAL
[realms]
EDBPEM.INTERNAL = {
kdc = krb5server.edbpem.internal
admin_server = krb5server.edbpem.internal
}
```Restart the database server to reflect the changes:
```shell systemctl restart <POSTGRES_SERVICE_NAME> ```
POSTGRES_SERVICE_NAME is the service name of the Postgres (PostgreSQL/EDB Postgres Advanced Server) database, for example, postgresql-13 for PostgreSQL 13 database on CentOS or RHEL or Rocky Linux platforms.
5. Obtain and view the initial ticket
The kinit utility obtains and caches Kerberos tickets. You typically use this utility to obtain the ticket-granting ticket, using a password you entered to decrypt the credential from the key distribution center (KDC). The ticket-granting ticket is then stored in your credential cache.
You can view the details of the ticket using the klist utility.
Note
You must install the Kerberos client on the PEM server and the client machine before using kinit and klist.
$ kinit <USERNAME@REALM> $ klist
It displays the principal along with the Kerberos ticket.
Note
The USERNAME@REALM specified here must be a database user having the pem_admin role and CONNECT privileges on the pem database.
6. Configure the PEM server
Run the PEM configure script on the PEM server to use Kerberos authentication:
```shell $ sudo PEM_APP_HOST=pem.edbpem.internal PEM_KRB_KTNAME=<PEM_INSTALLATION_DIRECTORY/share/pemserver.keytab <PEM_INSTALLATION_DIRECTORY>/bin/configure-pem-server.sh ```
In the config_setup.py file, configure PEM_DB_HOST and check that the value of PEM_AUTH_METHOD is set to 'kerberos'.
```shell $ sudo vim <PEM_INSTALLATION_DIRECTORY>/share/web/config_setup.py PEM_DB_HOST=`pem.edbpem.internal` ```
Configure HOST in the .install-config file.
```shell $ sudo vim <PEM_INSTALLATION_DIRECTORY>/share/.install-config HOST=`pem.edbpem.internal` ```
If the PEM server uses Kerberos authentication:
All the monitored servers default to use the same authentication. To override the default, in the
config_local.pyfile, add the parameterALLOW_DATABASE_CONNECTION_WITHOUT_KERBEROSand set it toTrue.All the authenticated user principals are appended with the realm (USERNAME@REALM) and passed as the database user name by default. To override the default, in the
config_local.pyfile, add the parameterPEM_USER_KRB_INCLUDE_REALMand set it toFalse.
Restart the Apache server:
```shell sudo systemctl restart <SERVICE_NAME> ```
Edit the entries at the top in pg_hba.conf to use the gss authentication method. Then reload the database server.
```shell host pem +pem_user <ip_of_pem_server>/32 gss host postgres +pem_user <ip_of_pem_server>/32 gss ``` ```shell systemctl reload <POSTGRES_SERVICE_NAME> ```
POSTGRES_SERVICE_NAME is the service name of the Postgres (PostgreSQL/EDB Postgres Advanced Server) database, for example, postgresql-13 for PostgreSQL 13 database on CentOS or RHEL or Rocky Linux platforms.
Note
You can't specify the connection type as hostgssenc. Windows doesn't support gss encrypted connection.
7. Browser settings
Configure the browser on the client machine to access the PEM web client to use the Spnego/Kerberos.
For Mozilla Firefox:
- Open the low-level Firefox configuration page by loading the
about:configpage. - In the search box, enter
network.negotiate-auth.trusted-uris. - Double-click the
network.negotiate-auth.trusted-urispreference and enter the hostname or the domain of the web server that's protected by Kerberos HTTP SPNEGO. Separate multiple domains and hostnames with commas. - In the search box, enter
network.negotiate-auth.delegation-uris. - Double-click the
network.negotiate-auth.delegation-urispreference and enter the hostname or the domain of the web server that's protected by Kerberos HTTP SPNEGO. Separate multiple domains and hostnames with commas. - Select OK.
For Google Chrome on Linux or MacOS:
Add the
--auth-server-whitelistparameter to thegoogle-chromecommand. For example, to run Chrome from a Linux prompt, run thegoogle-chromecommand as follows:google-chrome --auth-server-whitelist = "hostname/domain"
After configuring the PEM server, you can access the PEM web interface in your browser. Navigate to:
https://<ip_address_of_PEM_server>:8443/pem
Note
You might see the following error while connecting to your Postgres cluster:
psql -h hostname template1
psql: GSSAPI continuation error: Unspecified GSS failure. Minor code may provide more information
GSSAPI continuation error: Key version is not available
Add encryption types to the keytab using ktutil or by recreating the Postgres keytab with all crypto systems from AD.
- On this page
- 1. Install Active Directory, the PEM server, and the PEM backend database server
- 2. Create users in Active Directory to map with service principals
- 3. Extract key tables from Active Directory
- 4. Configure the PEM backend database server
- 5. Obtain and view the initial ticket
- 6. Configure the PEM server
- 7. Browser settings