Distributed high availability
Distributed high-availability clusters are powered by EDB Postgres Distributed. They use multi-master logical replication to deliver more advanced cluster management compared to a physical replication-based system. Distributed high-availability clusters let you deploy a cluster across multiple regions or a single region. For use cases where high availability across regions is a major concern, a cluster deployment with distributed high availability enabled can provide two data groups with a witness group in a third region.
This configuration provides a true active-active solution as each data group is configured to accept writes.
Distributed high-availability clusters support both EDB Postgres Advanced Server and EDB Postgres Extended Server database distributions.
Distributed high-availability clusters contain one or two data groups. Your data groups can contain either three data nodes or two data nodes and one witness node. At any given time, one of these data nodes in each group is the leader and accepts writes, while the rest are referred to as shadow nodes. We recommend that you don't use two data nodes and one witness node in production unless you use asynchronous commit scopes.
PGD Proxy routes all application traffic to the leader node, which acts as the principal write target to reduce the potential for data conflicts. PGD Proxy leverages a distributed consensus model to determine availability of the data nodes in the cluster. On failure or unavailability of the leader, PGD Proxy elects a new leader and redirects application traffic. Together with the core capabilities of EDB Postgres Distributed, this mechanism of routing application traffic to the leader node enables fast failover and switchover.
The witness node/witness group doesn't host data but exists for management purposes. It supports operations that require a consensus, for example, in case of an availability zone failure.
Note
Operations against a distributed high-availability cluster leverage the EDB Postgres Distributed switchover feature, which provides subsecond interruptions during planned lifecycle operations.
Single data location
A configuration with a single data location has one data group and either:
Two data nodes with one lead, one shadow, and a witness node, each in separate availability zones

Three data nodes with one lead and two shadow nodes, each in separate availability zones
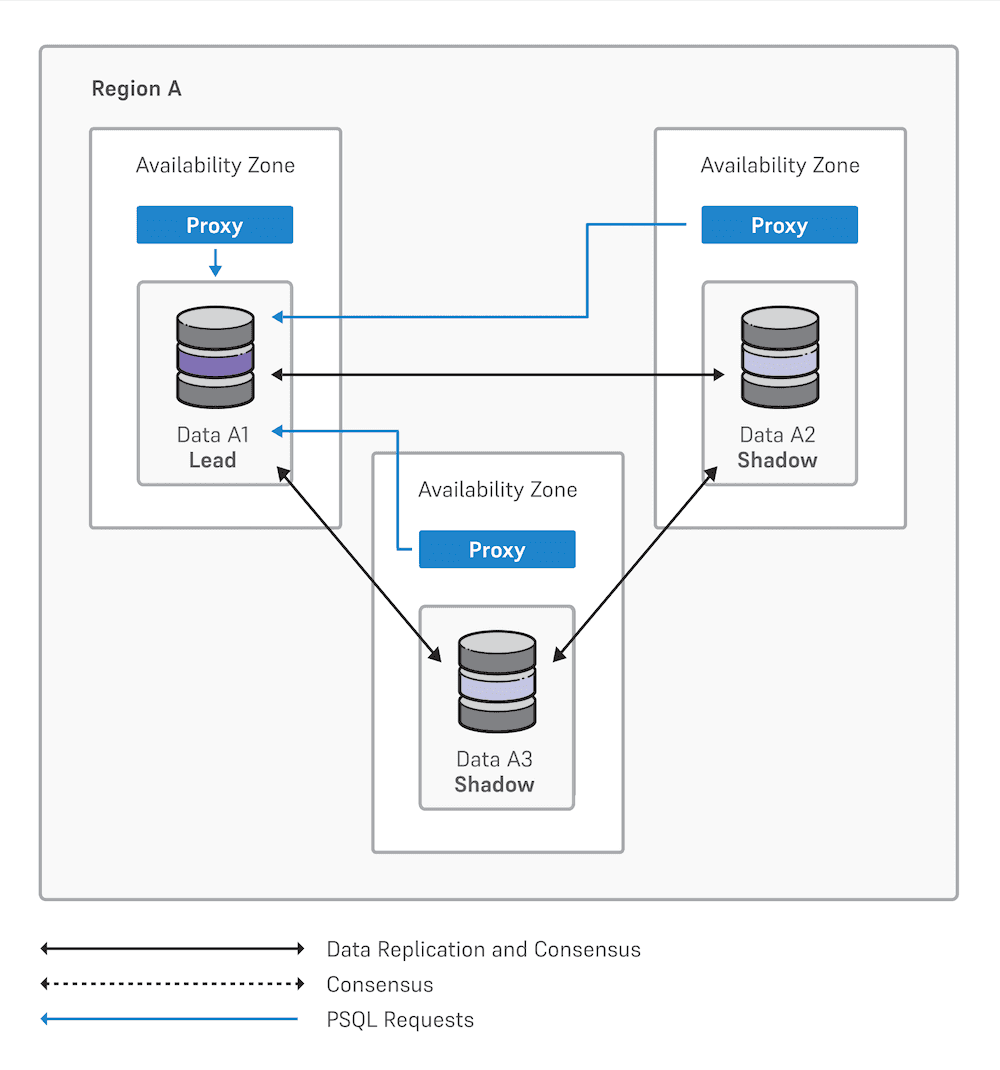
Multiple data locations and witness node
A configuration with multiple data locations has two data groups that contain either:
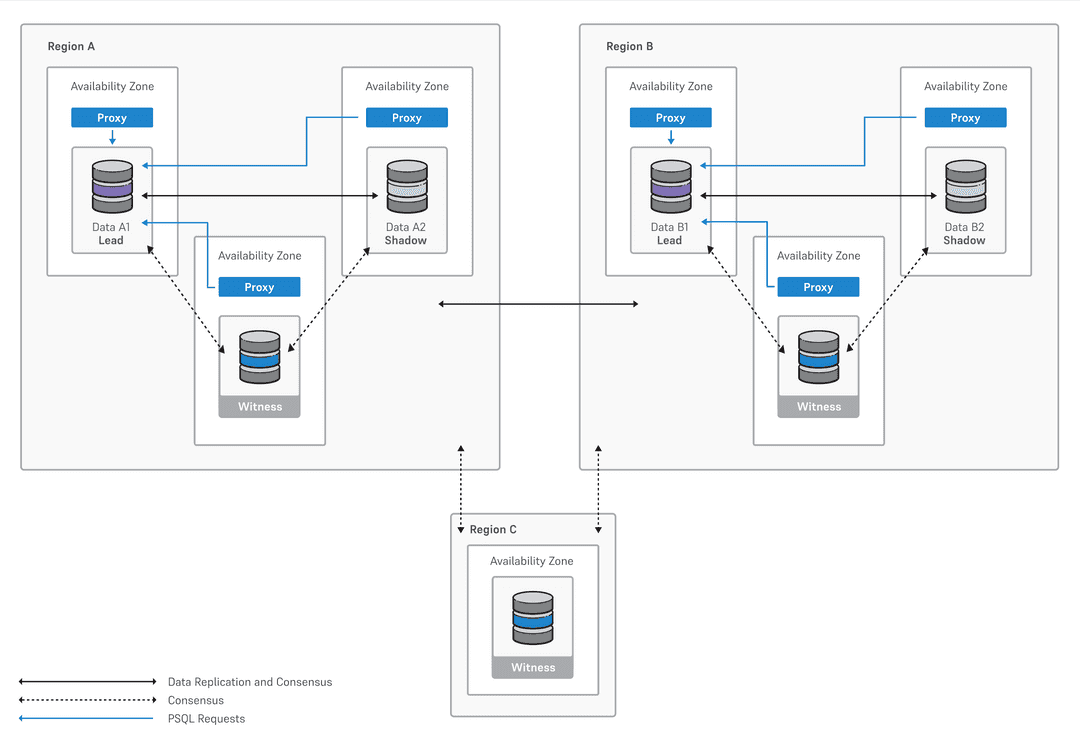
Three data nodes:
A data node and two shadow nodes in one region
The same configuration in another region
A witness node in a third region
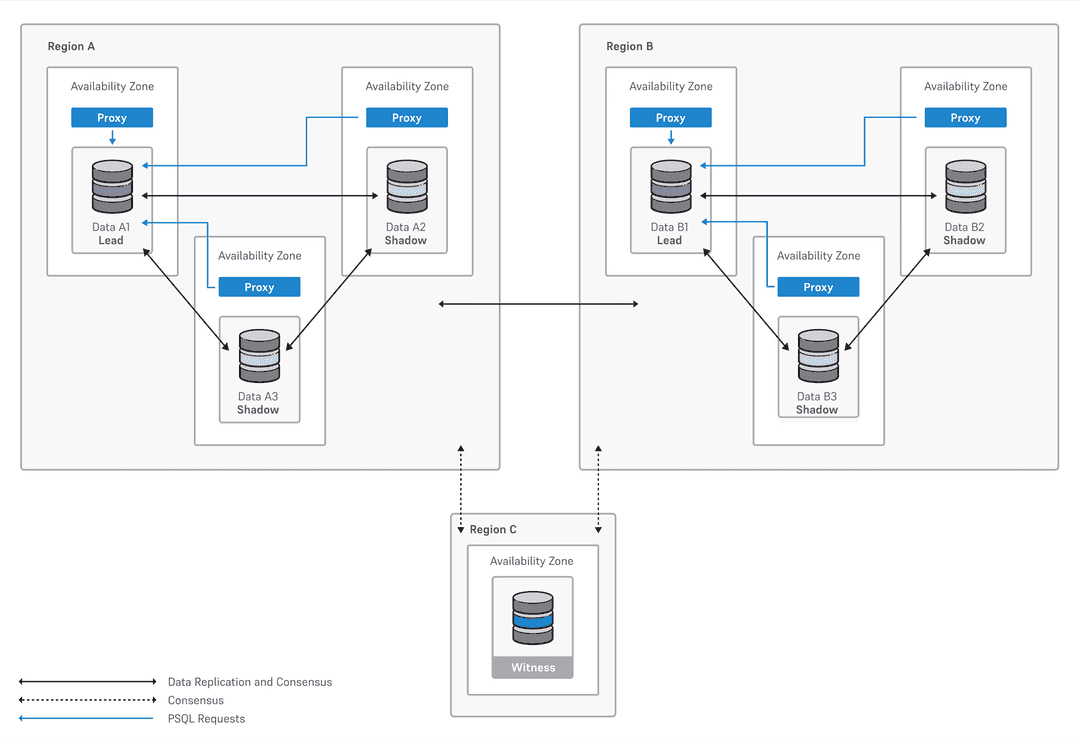
Two data nodes (not recommended for production):
A data node, shadow node, and a witness node in one region
The same configuration in another region
A witness node in a third region
Cross-cloud service providers (CSP) witness node
By default, the cloud service provider selected for the data groups is preselected for the witness node.
To guard against cloud service provider failures, you can designate a witness node on a cloud service provider different from the one for data groups. This configuration can enable a three-region configuration even if a single cloud provider offers only two regions in the jurisdiction you're allowed to deploy your cluster in.
Cross-cloud service provider witness nodes are available with AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud using your own cloud account and BigAnimal's cloud account. This option is enabled by default and applies to both multi-region configurations available with PGD. For witness nodes you pay only for the infrastructure used, which is reflected in the pricing estimate.
Read-only workloads
When you enable the read-only workloads option during the cluster creation, a read-only connection string is created for the data group. You can use this connection to allow your application or service to route read-only requests through the shadow nodes (non-write leaders) to lighten the load on the write leaders and improve the distributed high-availability cluster's performance.
If you have more than one data group, you can choose whether to enable the read-only workloads option on a per-data-group basis.
Since the infrastructure of a distributed high-availability cluster is almost entirely based on EDB Postgres Distributed, the same PGD Proxy read-only routing rules apply.
Important
Once you have configured a read-only connection string with your application, read-only workloads are routed to shadow nodes (non-write leaders). The connection is read-only because it accepts read-only queries through the shadow nodes. However, commands that run on read-only connections aren't filtered by BigAnimal, so shadow nodes can still perfom write operations to the contents of database tables. We recommend that you use a Postgres role with minimal read-only privileges for your application or pass default_transaction_read_only=on in the connection string. This way, you can avoid write operations on shadow nodes that could cause conflicts between the write leader and the shadow nodes.
IP addresses
If you're configuring read-only workload connections on your own cloud account, you might have to raise the IP address resource limits for the cluster:
For Azure, the IP address quota is standard public IP address.
For AWS, the IP address quota is Elastic IP. You might also have to increase the Network Load Balancers per Region value.
Advisory locks
Advisory locks aren't replicated between Postgres nodes, so advisory locks taken on a shadow node don't conflict with advisory locks taken on the lead. We recommend that applications that rely on advisory locking avoid using read-only workloads for those transactions.
For more information
For instructions on creating a distributed high-availability cluster using the BigAnimal portal, see Creating a distributed high-availability cluster.
For instructions on creating, retrieving information from, and managing a distributed high-availability cluster using the BigAnimal CLI, see Using the BigAnimal CLI.