Security example v16
In this example, a new database is created along with two users:
– hr_mgr, who owns a copy of the entire sample application in schemahr_mgrsales_mgr, who owns a schema namedsales_mgrthat has a copy of only theemptable containing only the employees who work in sales
The procedure list_emp, function hire_clerk, and package emp_admin are used in this example. All of the default privileges that are granted upon installation of the sample application are removed and then explicitly regranted so as to present a more secure environment.
Programs list_emp and hire_clerk are changed from the default of definer’s rights to invoker’s rights. Then, when sales_mgr runs these programs, they act on the emp table in the sales_mgr schema since the sales_mgr search path and privileges are used for name resolution and authorization checking.
Programs get_dept_name and hire_emp in the emp_admin package are then executed by sales_mgr. In this case, the dept table and emp table in the hr_mgr schema are accessed as hr_mgr is the owner of the emp_admin package which is using definer’s rights. Since the default search path is in effect with the $user placeholder, the schema matching the user (in this case, hr_mgr) is used to find the tables.
Step 1: Create database and users
As user enterprisedb, create the hr database:
CREATE DATABASE hr;
Switch to the hr database and create the users:
\c hr enterprisedb CREATE USER hr_mgr IDENTIFIED BY password; CREATE USER sales_mgr IDENTIFIED BY password;
Step 2: Create the sample application
Create the entire sample application, owned by hr_mgr, in the hr_mgr schema.
\c - hr_mgr \i /usr/edb/as16/share/edb-sample.sql BEGIN CREATE TABLE CREATE TABLE CREATE TABLE CREATE VIEW CREATE SEQUENCE . . . CREATE PACKAGE CREATE PACKAGE BODY COMMIT
Step 3: Create the emp table in schema sales_mgr
Create a subset of the emp table owned by sales_mgr in the sales_mgr schema.
\c – hr_mgr GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA hr_mgr TO sales_mgr; \c – sales_mgr CREATE TABLE emp AS SELECT * FROM hr_mgr.emp WHERE job = 'SALESMAN';
The GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA command allows sales_mgr access into the hr_mgr’s schema to make a copy of the hr_mgr emp table. This step is required in EDB Postgres Advanced Server and isn't compatible with Oracle databases. Oracle doesn't have the concept of a schema that's distinct from its user.
Step 4: Remove default privileges
Remove all privileges to later illustrate the minimum required privileges needed.
\c – hr_mgr REVOKE USAGE ON SCHEMA hr_mgr FROM sales_mgr; REVOKE ALL ON dept FROM PUBLIC; REVOKE ALL ON emp FROM PUBLIC; REVOKE ALL ON next_empno FROM PUBLIC; REVOKE EXECUTE ON FUNCTION new_empno() FROM PUBLIC; REVOKE EXECUTE ON PROCEDURE list_emp FROM PUBLIC; REVOKE EXECUTE ON FUNCTION hire_clerk(VARCHAR2,NUMBER) FROM PUBLIC; REVOKE EXECUTE ON PACKAGE emp_admin FROM PUBLIC;
Step 5: Change list_emp to invoker’s rights
While connected as user hr_mgr, add the AUTHID CURRENT_USER clause to the list_emp program and resave it in EDB Postgres Advanced Server. When performing this step, be sure you're logged in as hr_mgr. Otherwise the modified program might end up in the public schema instead of in the hr_mgr schema.
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDURE list_emp AUTHID CURRENT_USER IS v_empno NUMBER(4); v_ename VARCHAR2(10); CURSOR emp_cur IS SELECT empno, ename FROM emp ORDER BY empno; BEGIN OPEN emp_cur; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('EMPNO ENAME'); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('----- -------'); LOOP FETCH emp_cur INTO v_empno, v_ename; EXIT WHEN emp_cur%NOTFOUND; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(v_empno || ' ' || v_ename); END LOOP; CLOSE emp_cur; END;
Step 6: Change hire_clerk to invoker’s rights and qualify call to new_empno
While connected as user hr_mgr, add the AUTHID CURRENT_USER clause to the hire_clerk program.
Also, after the BEGIN statement, fully qualify the reference new_empno to hr_mgr.new_empno to ensure the hire_clerk function call to the new_empno function resolves to the hr_mgr schema.
When resaving the program, be sure you're logged in as hr_mgr. Otherwise the modified program might end up in the public schema instead of in the hr_mgr schema.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION hire_clerk ( p_ename VARCHAR2, p_deptno NUMBER ) RETURN NUMBER AUTHID CURRENT_USER IS v_empno NUMBER(4); v_ename VARCHAR2(10); v_job VARCHAR2(9); v_mgr NUMBER(4); v_hiredate DATE; v_sal NUMBER(7,2); v_comm NUMBER(7,2); v_deptno NUMBER(2); BEGIN v_empno := hr_mgr.new_empno; INSERT INTO emp VALUES (v_empno, p_ename, 'CLERK', 7782, TRUNC(SYSDATE), 950.00, NULL, p_deptno); SELECT empno, ename, job, mgr, hiredate, sal, comm, deptno INTO v_empno, v_ename, v_job, v_mgr, v_hiredate, v_sal, v_comm, v_deptno FROM emp WHERE empno = v_empno; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Department : ' || v_deptno); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Employee No: ' || v_empno); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Name : ' || v_ename); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Job : ' || v_job); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Manager : ' || v_mgr); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Hire Date : ' || v_hiredate); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Salary : ' || v_sal); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('Commission : ' || v_comm); RETURN v_empno; EXCEPTION WHEN OTHERS THEN DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('The following is SQLERRM:'); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(SQLERRM); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('The following is SQLCODE:'); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(SQLCODE); RETURN -1; END;
Step 7: Grant required privileges
While connected as user hr_mgr, grant the privileges needed so sales_mgr can execute the list_emp procedure, hire_clerk function, and emp_admin package. The only data object sales_mgr has access to is the emp table in the sales_mgr schema. sales_mgr has no privileges on any table in the hr_mgr schema.
GRANT USAGE ON SCHEMA hr_mgr TO sales_mgr; GRANT EXECUTE ON PROCEDURE list_emp TO sales_mgr; GRANT EXECUTE ON FUNCTION hire_clerk(VARCHAR2,NUMBER) TO sales_mgr; GRANT EXECUTE ON FUNCTION new_empno() TO sales_mgr; GRANT EXECUTE ON PACKAGE emp_admin TO sales_mgr;
Step 8: Run programs list_emp and hire_clerk
Connect as user sales_mgr, and run the following anonymous block:
\c – sales_mgr DECLARE v_empno NUMBER(4); BEGIN hr_mgr.list_emp; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('*** Adding new employee ***'); v_empno := hr_mgr.hire_clerk('JONES',40); DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('*** After new employee added ***'); hr_mgr.list_emp; END; EMPNO ENAME ----- ------- 7499 ALLEN 7521 WARD 7654 MARTIN 7844 TURNER *** Adding new employee *** Department : 40 Employee No: 8000 Name : JONES Job : CLERK Manager : 7782 Hire Date : 08-NOV-07 00:00:00 Salary : 950.00 *** After new employee added *** EMPNO ENAME ----- ------- 7499 ALLEN 7521 WARD 7654 MARTIN 7844 TURNER 8000 JONES
The table and sequence accessed by the programs of the anonymous block are shown in the following diagram. The gray ovals represent the schemas of sales_mgr and hr_mgr. The current user during each program execution is shown in parenthesis in bold red font.
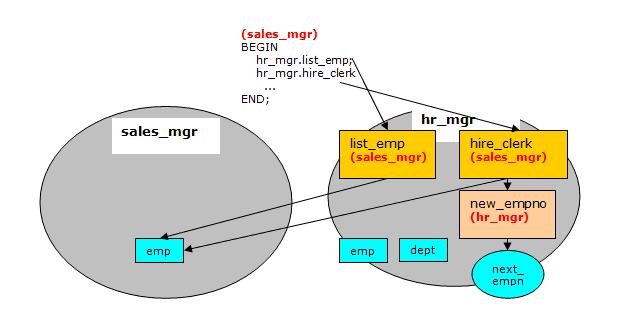
Selecting from the sales_mgr emp table shows that the update was made in this table.
SELECT empno, ename, hiredate, sal, deptno, hr_mgr.emp_admin.get_dept_name(deptno) FROM sales_mgr.emp;
empno | ename | hiredate | sal | deptno | get_dept_name -------+--------+--------------------+---------+--------+--------------- 7499 | ALLEN | 20-FEB-81 00:00:00 | 1600.00 | 30 | SALES 7521 | WARD | 22-FEB-81 00:00:00 | 1250.00 | 30 | SALES 7654 | MARTIN | 28-SEP-81 00:00:00 | 1250.00 | 30 | SALES 7844 | TURNER | 08-SEP-81 00:00:00 | 1500.00 | 30 | SALES 8000 | JONES | 08-NOV-07 00:00:00 | 950.00 | 40 | OPERATIONS (5 rows)
The following diagram shows that the SELECT command references the emp table in the sales_mgr schema. However, the dept table referenced by the get_dept_name function in the emp_admin package is from the hr_mgr schema since the emp_admin package has definer’s rights and is owned by hr_mgr. The default search path setting with the $user placeholder resolves the access by user hr_mgr to the dept table in the hr_mgr schema.

Step 9: Run program hire_emp in the emp_admin package
While connected as user sales_mgr, run the hire_emp procedure in the emp_admin package.
EXEC hr_mgr.emp_admin.hire_emp(9001, 'ALICE','SALESMAN',8000,TRUNC(SYSDATE),1000,7369,40);
This diagram shows that the hire_emp procedure in the emp_admin definer’s rights package updates the emp table belonging to hr_mgr. The object privileges of hr_mgr are used and the default search path setting with the $user placeholder resolves to the schema of hr_mgr.
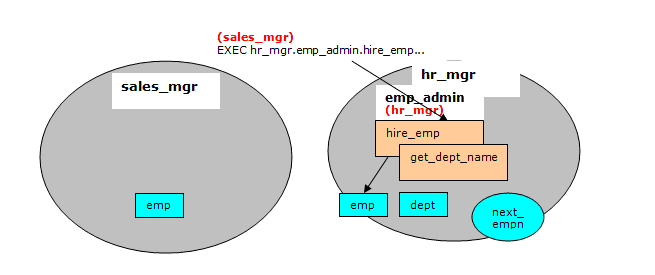
Now connect as user hr_mgr. The following SELECT command verifies that the new employee was added to the hr_mgr emp table since the emp_admin package has definer’s rights and hr_mgr is the emp_admin owner.
\c – hr_mgr SELECT empno, ename, hiredate, sal, deptno, hr_mgr.emp_admin.get_dept_name(deptno) FROM hr_mgr.emp;
empno | ename | hiredate | sal | deptno | get_dept_name -------+--------+--------------------+---------+--------+--------------- 7369 | SMITH | 17-DEC-80 00:00:00 | 800.00 | 20 | RESEARCH 7499 | ALLEN | 20-FEB-81 00:00:00 | 1600.00 | 30 | SALES 7521 | WARD | 22-FEB-81 00:00:00 | 1250.00 | 30 | SALES 7566 | JONES | 02-APR-81 00:00:00 | 2975.00 | 20 | RESEARCH 7654 | MARTIN | 28-SEP-81 00:00:00 | 1250.00 | 30 | SALES 7698 | BLAKE | 01-MAY-81 00:00:00 | 2850.00 | 30 | SALES 7782 | CLARK | 09-JUN-81 00:00:00 | 2450.00 | 10 | ACCOUNTING 7788 | SCOTT | 19-APR-87 00:00:00 | 3000.00 | 20 | RESEARCH 7839 | KING | 17-NOV-81 00:00:00 | 5000.00 | 10 | ACCOUNTING 7844 | TURNER | 08-SEP-81 00:00:00 | 1500.00 | 30 | SALES 7876 | ADAMS | 23-MAY-87 00:00:00 | 1100.00 | 20 | RESEARCH 7900 | JAMES | 03-DEC-81 00:00:00 | 950.00 | 30 | SALES 7902 | FORD | 03-DEC-81 00:00:00 | 3000.00 | 20 | RESEARCH 7934 | MILLER | 23-JAN-82 00:00:00 | 1300.00 | 10 | ACCOUNTING 9001 | ALICE | 08-NOV-07 00:00:00 | 8000.00 | 40 | OPERATIONS (15 rows)
- On this page
- Step 1: Create database and users
- Step 2: Create the sample application
- Step 3: Create the emp table in schema sales_mgr
- Step 4: Remove default privileges
- Step 5: Change list_emp to invoker’s rights
- Step 6: Change hire_clerk to invoker’s rights and qualify call to new_empno
- Step 7: Grant required privileges
- Step 8: Run programs list_emp and hire_clerk
- Step 9: Run program hire_emp in the emp_admin package