Monitoring using BigAnimal Observability
BigAnimal Observability is an integrated monitoring and alerting solution in BigAnimal. It's designed to monitor the performance of the Postgres clusters. It actively monitors various metrics of the Postgres clusters and triggers an alert as the defined thresholds are exceeded. This solution smoothly integrates into the BigAnimal ecosystem, using the vast amount of metric data that's gathered from Postgres clusters and their underlying infrastructure across all the regions.
BigAnimal Observability renders insightful charts that empower you to actively monitor each metric's behavior. It provides a streamlined path for you to take prompt and informed actions based on the generated alerts. This cohesive monitoring and alert system ensures comprehensive oversight and prompt responses in the BigAnimal environment.
When you log in, BigAnimal Observability monitoring widgets are displayed on the overview page on the project summary page. These widgets are available only for the deployed Postgres clusters and aren't available for the clusters in the provisioning process. They provide high-level, key information on:
- Memory
- CPU
- Storage usage percentages
- Transactions per second
- Database size
To see more in-depth metrics specific to the Postgres cluster, select any widget on the overview page. Selecting the widget opens the Monitoring and Logging tab of the cluster page.
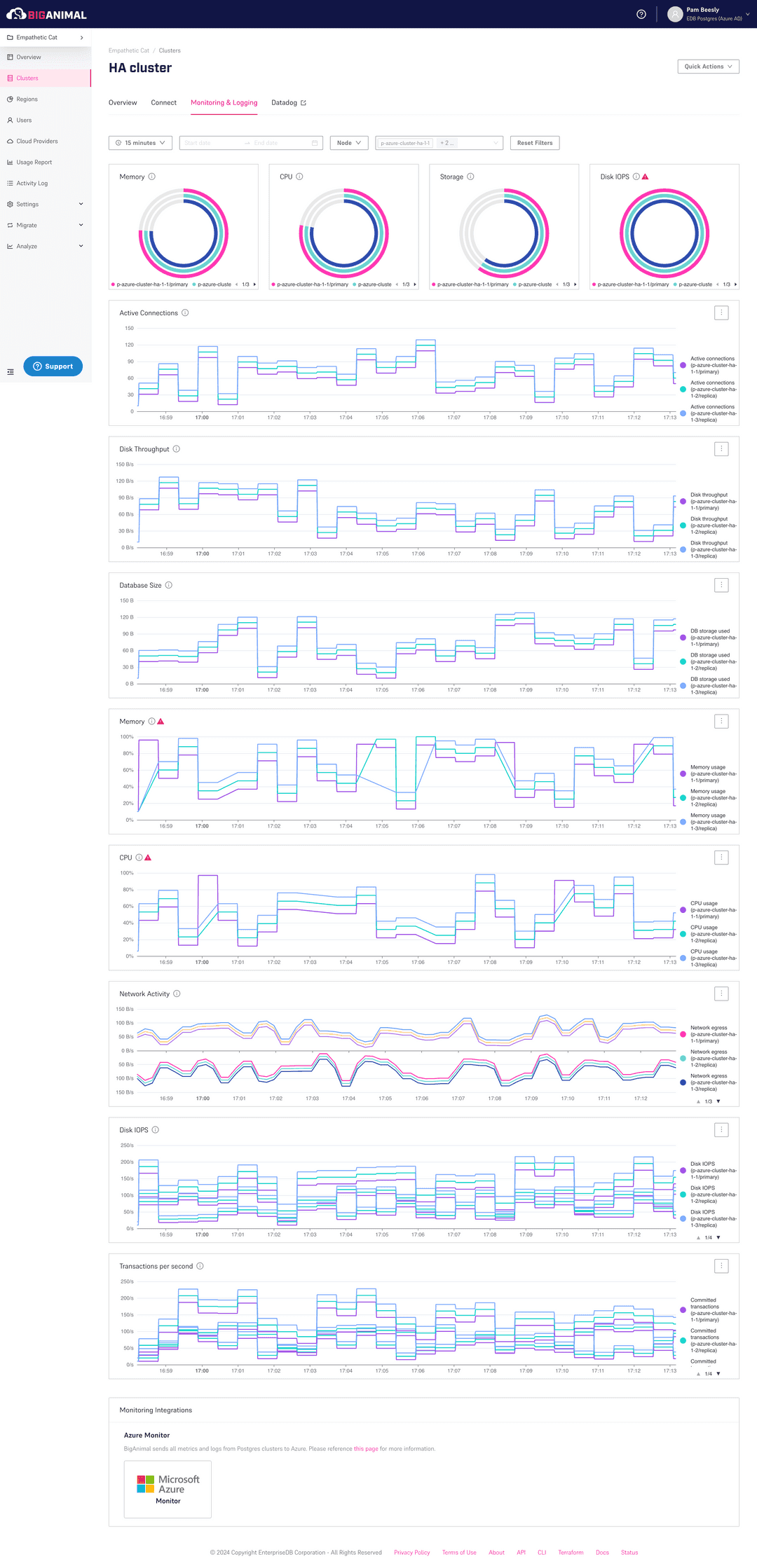
To view the Monitoring and Logging tab from the BigAnimal portal:
- In the left navigation of BigAnimal portal, go to Clusters.
- Select any ready cluster.
- On the cluster detail page, select the Monitoring and Logging tab.
The Monitoring and Logging tab displays the detailed monitoring metrics at a user-specified level of aggregation in the form of charts:
Levels of aggregation
To view the monitoring metrics at different levels, select any of these levels:
Cluster — This is the default level. It displays the aggregated metrics for the selected cluster to view a bigger picture of the system status.
Node — Select the node from the list at the top to display metrics for each node that composes a cluster. You can select one or more nodes using the button next to the node level. Selecting multiple nodes displays the metrics for each selected node on the chart using a different color for each node. Also, it displays whether a node is primary or replica on the charts.
Single-value charts
These charts display a specific single value based on the last value in the selected time interval. For example, if you choose Last N, the chart displays the current value. For the specific time interval, it displays the value at the end of that time interval. These charts display key metrics in text, gauges, or pie and donut form. They provide a concise snapshot of information such as:
- Memory (gauge chart) — The percentage of memory used by the Postgres cluster in the hosting node.
- CPU (gauge chart) — The percentage of CPU used by the Postgres cluster in the hosting node.
- Storage (gauge chart) — The percentage of the storage volume used by the Postgres cluster in the hosting node.
- Disk IOPS (gauge chart) — The disk I/O operations ratio of the total disk capacity per second for the Postgres cluster.
Historical charts
By default, these charts displays the historical data of the last 15 minutes. To view the historical data of a particular time range, customize the time range using a time-range picker. These charts display key metrics in single-line or multi-line form. They provide a concise snapshot of the information such as:
Memory (line chart) — The historical trend of memory usage percentage over a time period.
CPU (line chart) — The historical trend of CPU usage percentage over a time period.
Network activity (line chart) — The historical data transfer to and from the network card per second, over a time period.
Disk IOPS (line chart) — The historical trends in the number of reads, writes, and total operations on the disk per second, over a time period.
Transaction per second (line chart) — The historical trends in the number of transactions per second, over a time period.
Active connections (line chart) — The current number of connections between the client applications and the Postgres cluster.
Disk throughput (line chart) — The amount of data transferred to and from the disk per second for the Postgres cluster.
Database size (line chart) — The amount of storage volume used by the Postgres cluster.
Session wait states — These charts are powered by EDB wait states. They include:
- Wait times (line chart) — The approximate wait times for different wait events in a Postgres database, in seconds. This chart groups each wait event type to make it easy to compare and identify potential system issues.
- Wait events (line chart) — The approximate wait times of wait events in a Postgres database, in seconds.
Important
The EDB Wait States extension is enabled by default because it's needed to collect the data for session wait states charts. This extension gathers detailed information about the active sessions, including wait events. This information is then used to create charts for diagnostics purposes. For more information on enabling/disabling the extension, see EDB wait states.
Features for both types of charts
All these charts have tools and features that help you to get more information about the metrics or the chart. The time-range picker helps with viewing the data on these charts for a specific time-range interval. The different level helps to view the data on these charts at cluster and node level. The information tooltip helps you to view the information for a particular chart. The charts error state helps you to find the error and provides the option to edit the configurations and fix the error.
Time-range picker
To view the data of a particular time range configure the time range, on the Monitoring and Logging tab, use:
- The Last X list
- The date-time picker
The Last X list provides several time-range options. Each option in the list is enabled only after the specific time duration has elapsed since the Postgres cluster was created. The default time range is 15 minutes, and the maximum is Last 30 days.
Note
When you select the time range from the Last X list, the data on the Monitoring and Logging tab refreshes every 30 seconds.
Information tooltip
Each chart has an information tooltip that provides a detailed description of the chart. To view the information, hover over the tooltip icon on the right side of the chart name.
Charts error state
A red warning icon is displayed next to the tooltip if there's any error for that chart. If any of the metric exceeds its threshold, an error indicator appears. Selecting the red icon displays a window with a description of the error and an Edit Cluster button. Select Edit Cluster to go to the Edit Cluster page. Make the configuration changes based on the specific metric that brings the cluster to a healthy state.
The table shows a list of errors and the corresponding solutions.
| Error | Solution |
|---|---|
| High CPU | On the Edit Cluster page, select the preferred category, instance series, and the instance size to increase the CPU. |
| High Memory | On the Edit Cluster page, select the preferred category, instance series, and the instance size to increase the memory size. |
| High Storage | On the Edit Cluster page, go to the cluster settings and increase the volume size to increase the storage. |
| High Disk IOPS | On the Edit Cluster page, go to the cluster settings, volume properties and increase the IOPS within the allowed range. |
Features for historical charts
You can zoom the historical charts and also download the data of the historical charts.
Zooming charts
To zoom in an area on the historical chart, drag and select that specific area. To reset, select Reset zoom from the ellipsis menu at the top-right corner of the chart.
Download CSV
To download the metrics data used to produce the chart in CSV format, from the ellipsis menu in the top-right corner of the chart, select Download CSV. The download includes only the data currently visible on the chart. To download the different data, configure the time-range picker before selecting Download CSV.